Since joining UIUC in 1964 as an artist in residence, Professor Emeritus Shozo Sato 佐藤 昌三 has connected traditional Japanese arts with the world through his works and educational roles. Skilled in painting, calligraphy, theater, flower arrangement, and the tea ceremony, he introduced these art forms to the Champaign-Urbana community through many pioneering initiatives. For decades, his classes at UIUC gave students hands-on experience with various Japanese arts. He adapted and directed many Western classics into Japanese kabuki plays, which toured throughout the US and globally. He also founded and served as the first director of Japan House, the university’s beloved center for Japanese art and culture. Recently, his contributions have even extended to the University of Illinois Library’s collection.
In November 2023, Professor Sato donated his personal collection of approximately 500 volumes, primarily in Japanese, to the library. These donated books have greatly enhanced the University Library’s Japanese Studies collection due to their variety and uniqueness. They encompass various aspects of Japanese culture and art, and many have not previously been collected by North American institutions or are only found in a few collections. As the cataloging process nears completion, most of the books are now available to be checked out. They can be located by searching for “Shozo Sato Collection” in the University Library’s online catalog.
In honor of this valuable collection and Professor Sato’s contributions to the campus, the International and Area Studies Library has curated a special exhibit, with the co-sponsorship of the Japan House at the University of Illinois and the Center for East Asian and Pacific Studies. The exhibit, titled “Japanese Arts Through the Pages: An Exhibit of Shozo Sato’s Donated Book Collection,” is on display in Main Library Rooms 321 and 309 for the Spring 2024 semester.
This exhibit is arranged around four themes. Each theme showcases a Japanese art form closely related to Professor Sato’s career and highlights the notable strengths of his donated book collection.
Calligraphy and Sumi-e
Professor Sato’s donation to the University Library includes various guides, models, and scholarly works on a wide range of traditional and modern East Asian calligraphy and paintings, particularly sumi-e 墨絵 (black ink painting). The exhibition catalogs he collected over the years are also a valuable addition to our existing collections in Japanese arts. In this exhibit, we also showcase a collection of calligraphy items on loan from Japan House, alongside Professor Sato’s original sumi-e work, “Four Seasons.”

Ikebana
The Shozo Sato collection offers a remarkable glimpse into the rich history of ikebana 生け花 (flower arrangement) in Japan and beyond. It includes many rare illustrated books published in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, along with ikebana guides from various styles and schools, notably the Ikenobo 池坊 and the Ryusei 竜生 schools in Japan. Professor Sato, who worked closely with the grandmaster of the Ryusei School, Kasen Yoshimura 吉村 華泉, has donated many of Yoshimura’s works.
Although we cannot display any real flowers in the case, ikebana items from Japan House are on view.
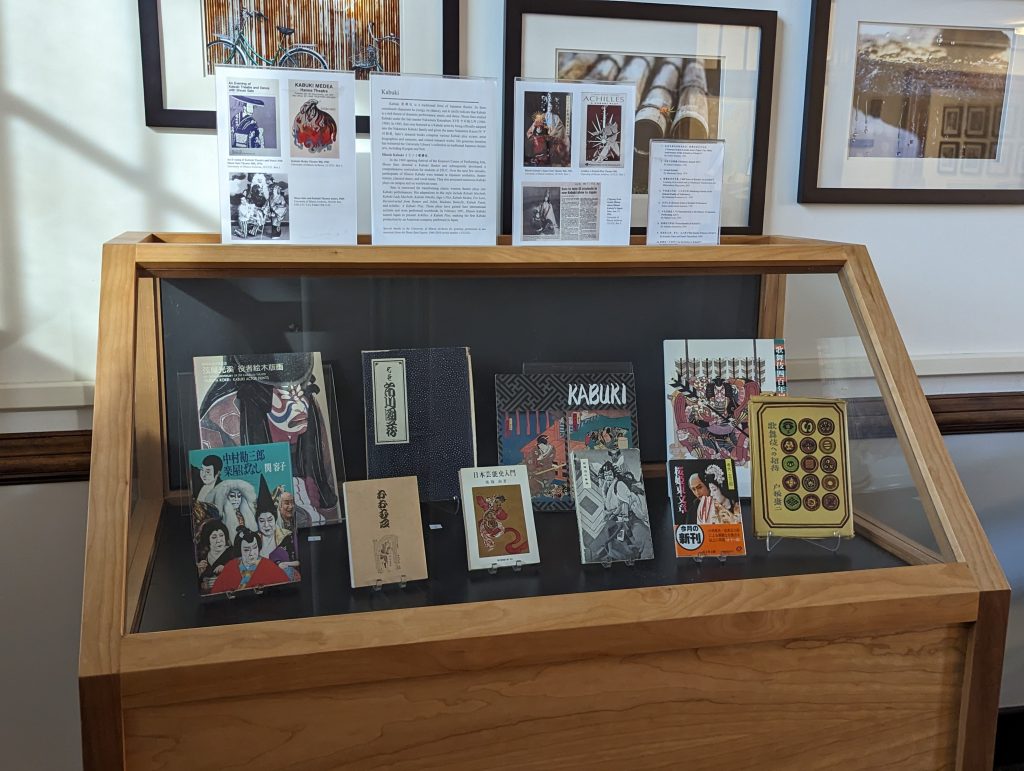
Kabuki
Kabuki 歌舞伎 is a traditional form of Japanese theater that combines dramatic performance, music, and dance. The Shozo Sato collection encompasses many kabuki play scripts, artist biographies, memoirs, and related research works. It has also expanded the University Library’s resources in other traditional Japanese theater arts, including bunraku 文楽, kyogen 狂言, and noh 能.
Alongside the books, we also display photos from the Shozo Sato Papers in the University of Illinois Archives to showcase Professor Sato and UIUC students’ involvement in kabuki over the years.
Tea Ceremony
The collection covers a broad range of topics related to the art of the tea ceremony, including its history, procedures, equipment, tea room design, Kaiseki meals, and Zen aesthetics. Having studied the tea ceremony with the Dai Nihon Chado Gakkai 大日本茶道学会 (The Grand Japan Tea Ceremony Society), Professor Sato’s donation also includes numerous rare materials published by the society. In addition, our exhibit features a set of chadogu 茶道具 (tea ceremony items) provided by Japan House.
IAS is grateful to our co-sponsor, Japan House at the University of Illinois, for loaning items and photos for the display. The Center for East Asian and Pacific Studies has also provided support for this exhibit.
Japan House at the University of Illinois
Center for East Asian and Pacific Studies
To explore more about Professor Sato’s career and works, see:
Shozo Sato Papers, 1964-2010, Series Number 12/12/21, University of Illinois Archives
Special thanks to Alice Tierney-Fife for her contributions in the preparation of this post.