This blog post is a follow-up to a post from last semester about the Honduras Water Project. This course, which provides students the chance to see how learning can have real life applications, is an extremely unique opportunity for students at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.

A University of Illinois flyer for the Honduras Water Project course
The two-semester long course is supported by the College of Engineering and included a research trip to Cerro Verde, Honduras over winter break. A small group of students was accompanied by professors Ann-Perry Witmer and Keilin Jahnke in visiting the small community site. While there we conducted surveys, both technical and social, and also included a health education workshop to work in correlation with our studies from the fall semester and also to aid in our efforts for this spring semester as well.
During our 10 days there, we lived in the community with the local people and stayed in a regional home, living on dirt floors without a shower for 10 days. Through this experience, we were able to see just a small amount of what life is like in the community. We built friendships and mutual respect during our time in Cerro Verde, and we left with new friendships and a greater drive to complete this project of developing a reliable water distribution system. Students representing each of the four divided teams– social, political, water, and structures– carried out various tasks during the trip to collect needed information for the water distribution system, and also to conduct health education workshops in the community.
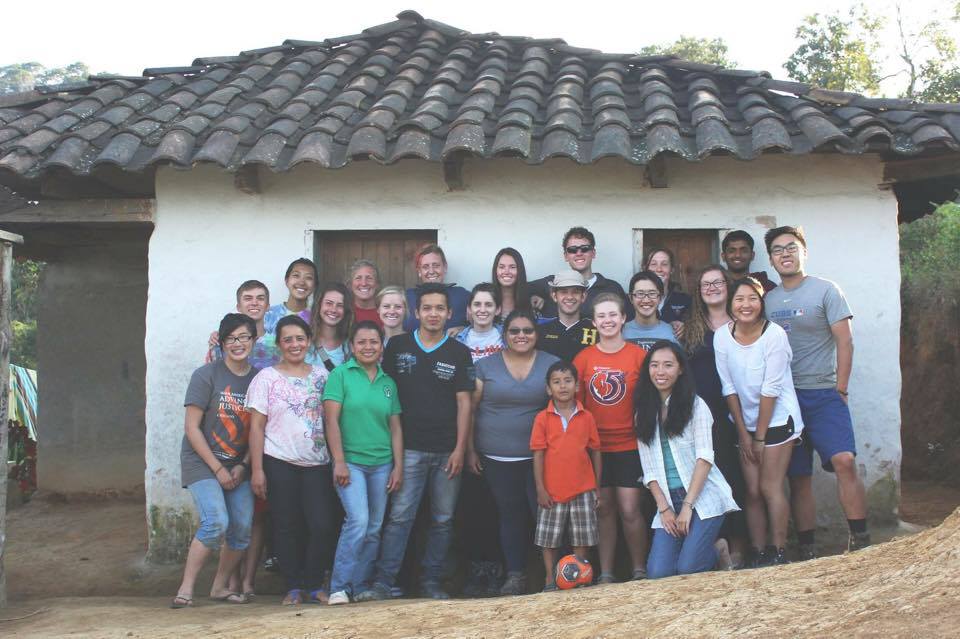

The University of Illinois students, faculty, and our friends from our partnering nongovernmental organization, Agua y Desarrollo Comunitario (ADEC) [Water and Community Development] Photo Credit: Jesse Han
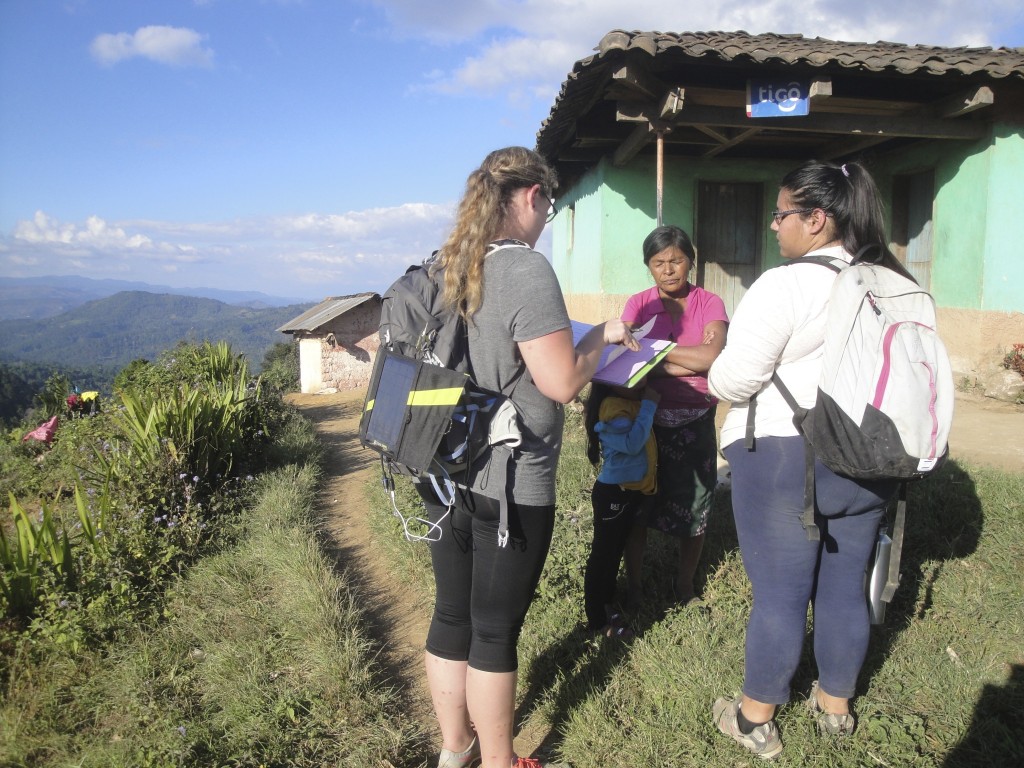

Two members of the Social team, Wendy Vergara and Ashley Adams, conducting household surveys in the community.
Photo Credit: Keilin Jahnke
The social team also conducted a health education workshop with the help of Oneida Lara Garcia, one of the water quality specialists for our partnering nongovernmental organization, Agua y Desarrollo Comunitario (ADEC) (Water and Community Development). The workshop was originally intended for children, but was expanded when nearly the entire community came to participate.
When asked about the importance of educational workshops in collaboration with international projects, Wendy Vergara, a sophomore in natural resources and environmental science said,
“It’s easy to overlook some of the resources we have in America. When it comes to early education, we don’t second guess it. Not something you think about because it’s required. It’s a resource that is given and provided to nearly everyone in the States. So when you visit a community like Cerro Verde, who only has one school room for all the children, you start to see the opportunities you have that they don’t. These school rooms are very limited in supplies and staff. The community doesn’t have their own teacher, but instead a teacher from a nearby community volunteers their time. This teacher tries to teach all grades at once, and you can feel how difficult that can be. Educational workshops further develop community members’ skills, and allow for information to be communicated to both children and adults. They provide visual knowledge essential to the community such as chlorinating water. Especially due to minimal literacy rates, some people may misuse products or go by word of mouth, which poses a threat to their health. Workshops can help decrease miscommunication and promote a safe space for them to ask questions.”
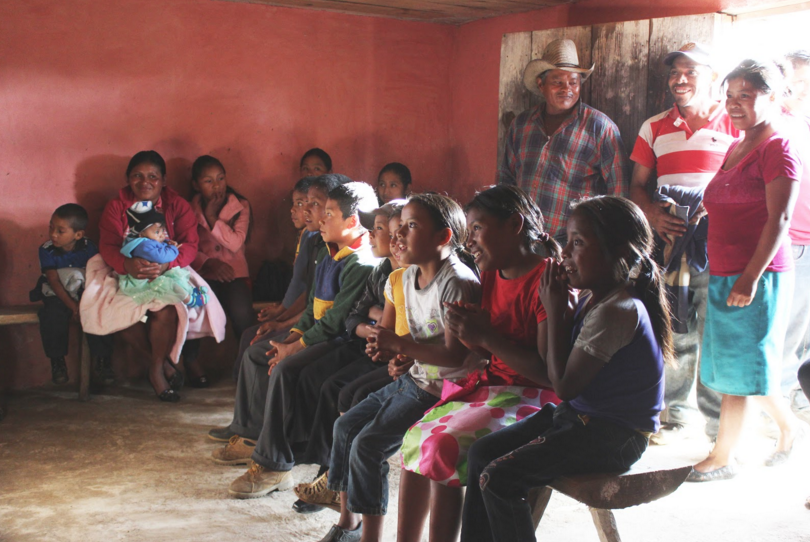

Children and community members gathered for the health education workshop.
Photo Credit: Jesse Han
The structures team had the opportunity to do the most hiking out of all the teams, although all of us got good exercise climbing through the mountainous area. They surveyed all the points in the community that could be included in the water distribution system. After finishing, two architecture students were able to create a more accurate map of all the houses on site. The Patronato, or, community leaders, requested a copy to post in their community building as well.
Kelsey Schreiber, a senior in general engineering, when discussing the the biggest challenge for the structures team said,
“The most difficult task. . . was ensuring that all of the homes being serviced were properly accounted for and surveyed. Between finding remote homes, distinguishing between current and future plots, and getting the correct homeowner names, we were never quite sure if we had all the correct information. Similarly, climbing the hills every day was brutal but built character.”
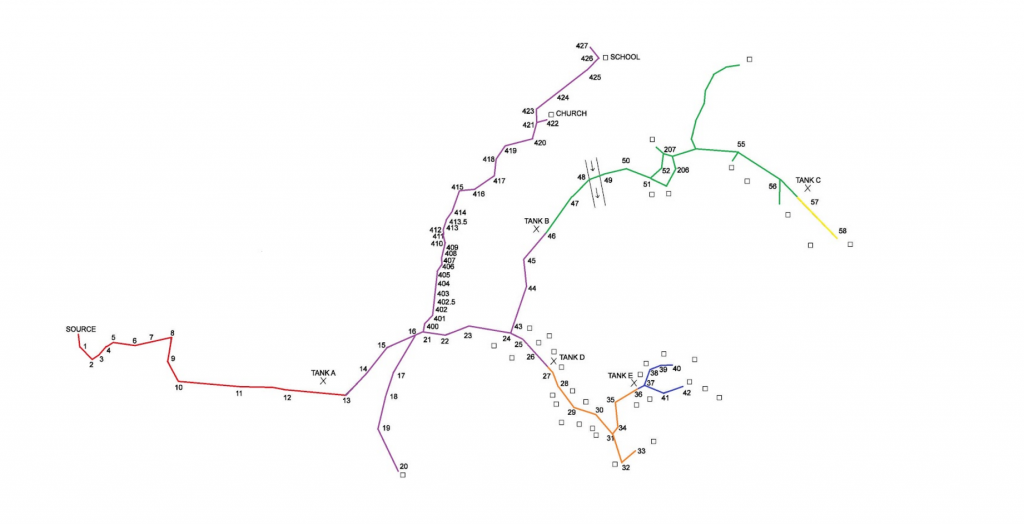
The nearly finalized schematic of the water distribution system pipelines throughout Cerro Verde.
The water team spent most of its time at the water source which was higher up in the mountains. They performed various tests for flow rate and water quality to help decide which source would be best suited for the system.
When asked what the most interesting thing about the trip to Cerro Verde was, Rahul Koshy, a junior in molecular and cellular biology said,
“We were exposed to people who grew up in a different culture and lived a different lifestyle, but there was definitely an underlying similarity between these and the people I’ve known all my life. I found that it was really easy to relate to the members of Cerro Verde even though they had a very different background than me. This is a small thing to learn, but it has changed the way I view people on the news, people on the streets, people in my life etc.”
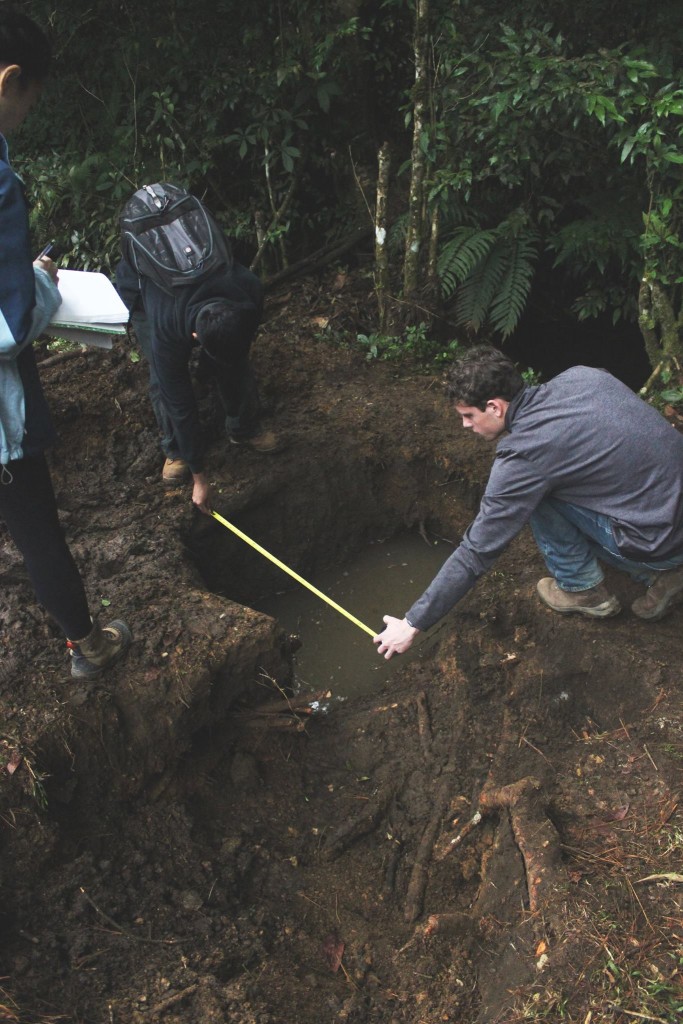

The water team taking measurements and doing testing at a potential source.
Photo Credit: Jesse Han
The political team also had an important job, working with the Patronato. It worked to make sure that there was complete transparency between the community, our class, and the NGO. It is imperative for this course, and for international projects, that the community take ownership of the project and that they are involved in every aspect of the planning, design, and implementation. An exciting accomplishment this year was that for the first time in Honduras Water Project’s history that the political team was able to draft and sign a complete agreement with the community and ADEC while still in Honduras.
Samantha Morrow, a senior in earth, society, and environmental sustainability and also global studies, when asked what benefit there is for having a signed agreement has for the project said,
“The written agreement is extremely important to the project for multiple reasons. Signing this document while we were in Cerro Verde allowed the Patronato and community to have physical evidence of our commitment to this project. This document keeps all parties accountable for their stated responsibilities and will protect the rights of all parties. Without this document the community might lose faith that this project will move forward or believe that we are not committed to the project. Additionally, this document allows us to hold the community accountable to protecting the system and maintaining its sustainability.”

The signed agreement between the community of Cerro Verde, ADEC, and the University of Illinois’ Honduras Water Project class.
The fall semester of our course consisted of preliminary research and also preparations for the trip in January 2016. This semester we have focused on creating the most appropriate system for the community. Our class has been in constant contact with ADEC, as well as the community regarding every step and decision in the design process.
Keilin Jahnke is a PhD student in Agricultural and Biological Engineering, and professor for the course. When asked what benefit can come from spending time in the community that one is working with for an international engineering project, she responded saying,
“It can be easy to sit in a classroom thousands of miles away from the community that you are working with and think of nothing else besides the technical components of the project. But actually experiencing the community, living with the people you are working with, gives you the social and cultural context that is vital for the project’s success. No longer are you just working on an engineering project, you are acting as a consultant to real people who have real lives, real intricacies, real needs.”
-

-
HWP students waiting for a meeting at the community center. — Photo Credit: Keilin Jahnke
-

-
UIUC students and Cerro Verde’s Patronato (community leaders) meeting to talk at the community center. — Photo Credit: Jesse Han
-

-
The source of water for Maria, the community member who owns the lowest house in Cerro Verde. — Photo Credit: Jesse Han
-

-
Hiking to the potential sources. — Photo Credit: Keilin Jahnke
-

-
Working with our ADEC partners to do water quality testing of the potential sources. — Photo Credit: Jesse Han
-

-
Drawing “things that can be washed” during the health education workshop. — Photo Credit: Jesse Han
-

-
Comparing maps to create an accurate representation of the houses in the community. — Photo Credit: Jesse Han
-

-
Two architecture students, Jesse Han and Vicky Su, created a hand drawn map to leave with the community. — Photo Credit: Jesse Han
This course, ENG 398/498: Honduras Water Project, is led every year and is open to all students.It not only teaches you new technical knowledge, but it can also provide new perspectives about approaching international work. It has has encouraged me to pursue a master degree in engineering as these efforts blend STEM and interdisciplinary studies, and always promote a holistic approach towards international projects.
To hear more about the final design for the water distribution system for Cerro Verde come to the John Deere Pavilion onTuesday, May 3, 2016 from 4:00- 6:00 p.m. Everyone is welcome! For additional information, visit the Honduras Water Project website and/or contact Professor Ann-Perry Witmer.

Flyer for the course’s final presentation May 3, 2016