Soluble Lipid Bilayer Systems for Structural and Functional Studies of Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins have been historically difficult to study from a mechanistic perspective as many of the biophysical and chemical techniques applicable to soluble enzymes fail to deal with insoluble aggregates. Ideally, one would prefer to have a membrane protein of interest in a solubilized state for ease in purification, assay and the use of various biophysical methods and spectroscopies, crystallization for structure determination and biochemical manipulations that maintain the target protein in a stable state. Over the years, membrane protein solubilization has tended to use detergents to form mixed detergent-protein-lipid micelles. However, detergent poses a hazard to membrane protein stability and the excess micellar phase can interfere with many assay techniques and often has non-ideal optical properties (absorbance and light scattering) as well as the undesired partitioning of substrates and products. Detergent also presents technical obstacles during the manipulation of membrane proteins as they often co-concentrate with the protein target and can lead to inactive or denatured entities. Furthermore, many membrane protein systems require specific types of phospholipids to maintain active function. Liposome preparations have been used to incorporate membrane proteins and this approach has been found to be useful when compartmentalization of each side of the bilayer is needed, as for example in the assay of ion channels. However liposomes are large, unstable and difficult to prepare with precisely controlled size and stoichiometry. Nanodisc technology offers a solution to some of these challenges. In this approach, the membrane protein target is transiently solubilized with a detergent in the presence of phospholipids and an encircling amphipathic helical protein belt, termed a membrane scaffold protein (MSP). When the detergent is removed, typically by adsorption to hydrophobic beads, the target membrane protein simultaneously assembles with phospholipids into a discoidal bilayer with the size controlled by the length of the MSP. The membrane protein finds itself in a native membrane environment and the entire entity is rendered soluble via the encircling MSP belt. Over the past decade, this technology has proven applicable to a wide variety of membrane protein classes as evidenced by the abbreviated pictorial gallery shown below. Additional information on individual systems and various review articles can be found in our publication list. We continue to develop this important technology by engineering MSPs to make larger and smaller Nanodiscs, quantitating the lipid and protein exchange between discs, investigating the structure and homogeneity of assembled lipoprotein complexes and defining the kinetics of assembly using a combination of theory and experimental methodologies.
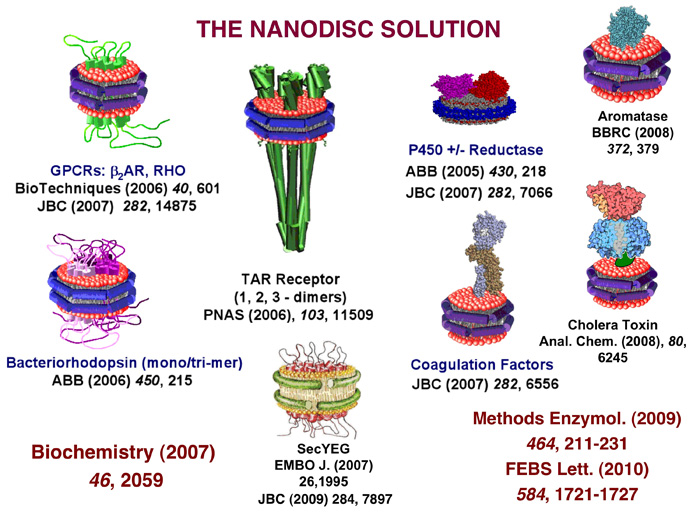
We have published several review articles over the past five years that summarize these successes and provide the protocols for use of Nanodiscs. Some of these are available through the PubMed links below:
- Sligar, S.G. and Denisov, I.G. (2020) “Nanodiscs: A Toolkit for Membrane Protein Science” Protein Science 30, 297-315
- Denisov, I.G., Schuler, M.A. and Sligar, S.G. (2019) “Nanodiscs as a New Tool to Examine Lipid-Protein Interactions” in Kleinschmidt, J. (ed.) Methods in Molecular Biology 2003, 645-671
- Denisov, I.G., and Sligar, S.G., (2010) “Cytochromes P450 in Nanodiscs.” Biochem. Biophys. Acta., 1814, 223-229. PMID: 20685623
- Ritchie, T.K., Grinkova, Y.V., Bayburt, T.H., Denisov, I.G., Zolnerciks, J.K., Atkins, W.M., and Sligar, S.G. (2009) “Reconstitution of Membrane Proteins in Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs.” Methods, Enzymol., 464, 211-231. PMID: 19903557
- Bayburt, T. H., and Sligar, S. G. (2009) “Membrane Protein Assembly into Nanodiscs.” FEBS Letters, 584(9), 1721-7. PMID: 19836392
- Nath, A., Atkins, W. M., and Sligar, S. G. (2007) “Applications of Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs in the Study of Membranes and Membrane Proteins.” Biochemistry, 46, 2059-2069. PMID: 17263563
- Schuler, M.A., Denisov, I.G. and Sligar, S.G. (2013) “Nanodiscs as a new tool to examine lipid-protein interactions.” Methods Mol. Biol., 974, 415-433. PMID: 23404286
- Denisov, I.G. and Sligar, S.G. (2016) “Nanodiscs for structural and functional studies of membrane proteins.” Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 23, 481-486. PMID: 27273631
- Luthra, A., Gregory, M, Grinkova, Y.V., Denisov, I.G. and Sligar, S.G. (2013) “Nanodiscs in the studies of membrane-bound cytochrome P450 enzymes.” Methods Mol. Biol., 987, 115-127. PMID: 23475672
We remain committed to the widest possible dissemination of the Nanodisc technology, including materials, methods and latest data from our laboratory. The Nanodisc system is now being used by hundreds of laboratories around the world that have realized great success and further advanced the technology.
Nanodisc Bibliography
The above listed reviews provide a detailed link to publications using this MSP-based Nanodisc technology.
Working with Nanodiscs
The genes that are used to generate the most common and useful Membrane Scaffold Proteins (MSP) are available at minimal cost from AddGene (https://www.addgene.org). These synthetic genes can yield hundreds of milligrams of MSP through simple E. coli fermentation. You can also obtain the purified Membrane Scaffold Proteins and reagents from Sigma Chemical Company.
An overview of the Nanodisc methods and guidance for self-assembling your favorite target protein into lipoprotein particles can be obtained through the following link:
OVERVIEW OF NANODISC TECHNOLOGY
Commercial Licensing of Nanodisc Technology
Nanodisc technology, and many of its uses, are covered by a broad intellectual property portfolio. Currently, the following patents have issued:
| 7,691,414 | Membrane scaffold proteins |
| 7,662,410 | Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins |
| 7,622,437 | Tissue factor compositions and methods |
| 7,592,008 | Membrane scaffold proteins |
| 7,575,763 | Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins |
| 7,083,958 | Membrane scaffold proteins |
| 7,048,949 | Membrane scaffold proteins |
The licensing rights to the entire intellectual property suite related to Nanodisc technology is held by the University of Illinois, and not by any private entity. At present, no exclusive licenses have been granted to the private sector, although many non-exclusive licenses are in place. The University’s Office of Technology Management is actively seeking the licensing and commercialization of this technology. Information for licensing Nanodisc technology for commercial, or for Materials Transfer Agreements, please contact:
Office of Technology Management
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
319, Ceramics Building MC-243
105 S. Goodwin Avenue
Urbana, IL 61801-2901
Phone: (217) 333 7862
Fax: (217) 265 5530
otm@illinois.edu
If you need any further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact our senior technical person for MSP production and Nanodisc assembly (Yelena Grinkova: grinkova@illinois.edu).
