Incoherent quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) measurements of pure, eutectic FLiNaK have been performed at the Spallation Neutron Source at Oak Ridge National Laboratory using the Cold Neutron Chopper Spectrometer (CNCS). The FLiNaK was sealed under vacuum in graphite-coated quartz tubes. These tubes were loaded into a niobium sample can that was mounted to the CNCS furnace stick. An example of the sealed FLiNaK is shown in Figure 1. QENS measurements were performed at 500, 600, 700, and 800 ºC. Three incident energies, 1.55, 3.32, and 12.0 meV, were used in the high flux mode of the CNCS. The energy resolution at 1.55 and 3.32 meV are approximately 55 and 110 meV, respectively. The 12.0 meV measurements were done to observe the static structure factor of the salt in an effort to observe phonon dispersion.

Figure 1. QENS samples 6 and 7 sealed in graphite-coated quartz tubes.
The measured QENS intensity is shown in Figure 2. A clear broadening with temperature is observed, indicated that the dynamics associated with diffusion is increasing. The effect of Ce addition (Ce is a actinide surrogate and a high-yield fission product) is to reduce these dynamics to the point where the QENS intensity collapses into the resolution function.
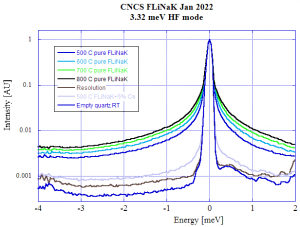
Figure 2. QENS data normalized to one at E=0. The figure legend shows the different temperatures. The resolution measurement is the sample at ambient temperature. The effect of 5 molar percent Ce is a significant reduction in dynamics and associated QENS intensity. An empty quartz tube at ambient temperature was also measured.