The 651 total buildings owned by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign stretch across an area of 9.9 square miles, or 6,370 acres. With a campus as large as ours, it’s no wonder the students, faculty, and staff use so many different means of transportation. Cars, bikes, skateboards, public transit, scooters – you name it!
When the weather is even halfway decent, you can find me biking around campus. It’s quick, convenient, and provides a bit of exercise in the otherwise sedentary life of a grad student. However, biking on campus is not without its frustrations. Bike routes are not always obvious, and sometimes they’re blocked by pedestrians or poorly parked cars. Even though I’ve gained more confidence in using bike lanes, it’s always a little nerve-wracking when I need to merge into traffic to turn left, or when a bus drives by and I’m stuck between it and a row of parked cars, the doors of which could open at any moment.
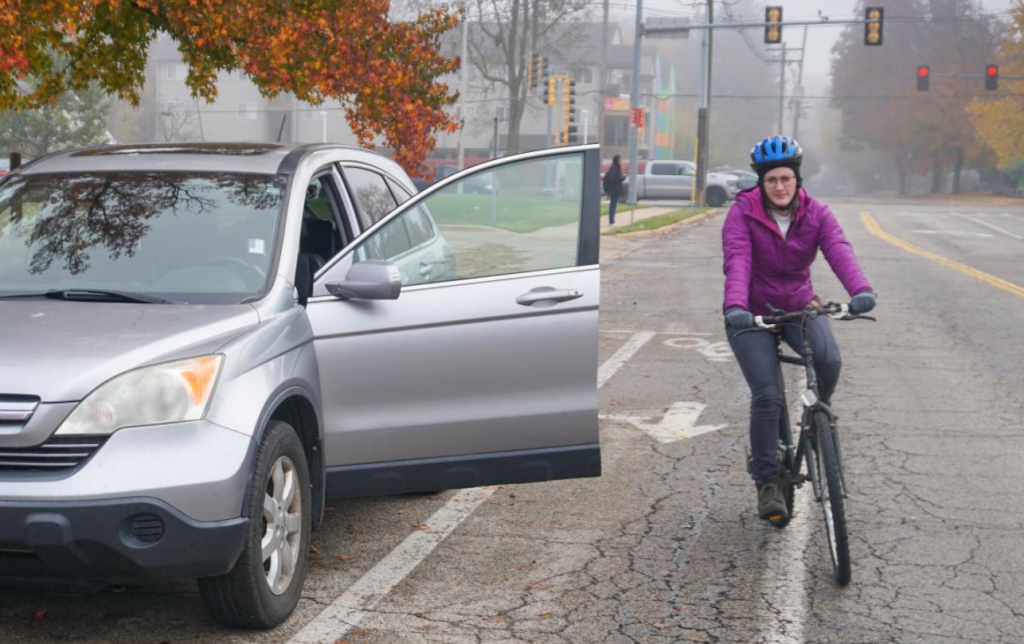

With these concerns in mind, I set out to learn more about the different kinds of bike routes on campus and the safety pros and cons of each. I read various research articles and made observations of potential features or issues while biking around campus. I took photos of campus bike routes, including common bike lane hazards, some of which were staged for the sake of photography, but still very real issues. I learned about resources related to getting around campus, and wanted to further share them.
In order to present my research, which relied heavily on maps, I used ArcGIS StoryMaps. This software was well-suited to the needs of this project. I was able to get data on bike routes and parking areas from campus facilities, which I used to create web maps with ArcMap and ArcGIS Online so that viewers could see each type of bike route in isolation. Continuity of bike routes has been found to be an important factor in whether people choose to bike, and certain people may feel more or less comfortable using different types of routes, so I wanted to demonstrate how these comfort limitations affect route continuity, possibly leading to fewer people choosing to bike.
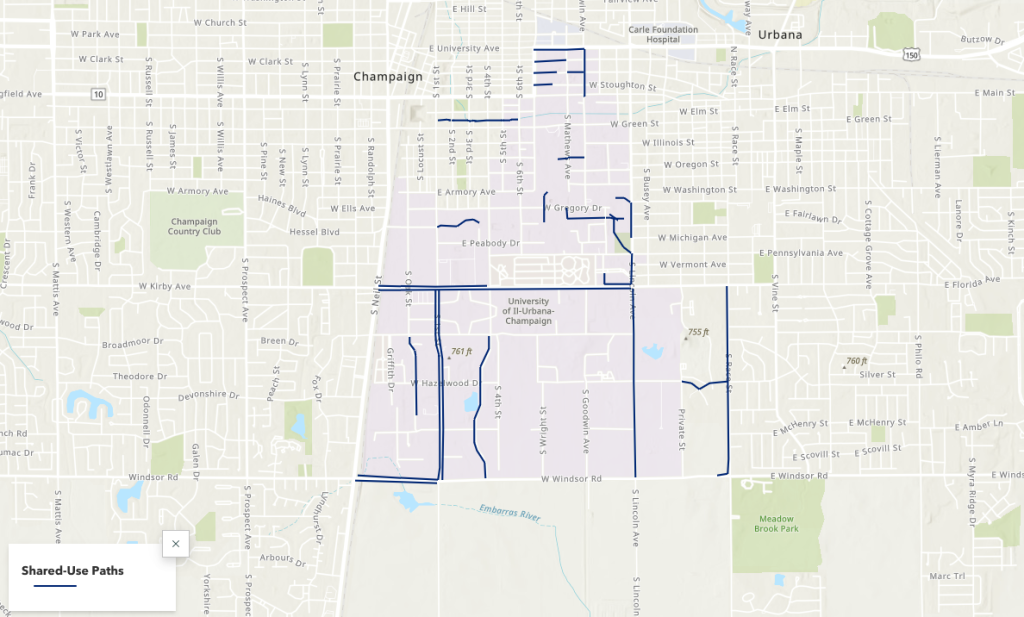
These maps, photos, and narrative elements came together to tell a story about biking on campus. To learn more about the campus bike network, the safety pros and cons of different bike route types, and campus navigation tips, you can explore the StoryMap here.