In the 21st century, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software has fundamentally changed how we search for information. OCR is the process of taking images with text and making them searchable. The implications of OCR vary from allowing searchability on massive databases to promoting accessibility by making screen readers a possibility. While this is all incredibly helpful, it is not without fault, as there are still many challenges to the OCR process that create barriers for certain projects. There are also some natural limitations to using this software that especially have consequences for time-sensitive projects, but other factors within human control have negatively influenced the development of OCR technology in general. This blog post will explore two issues: the amount of human labor required on an OCR project and the Western biases of this kind of software.
Human Labor Requirements
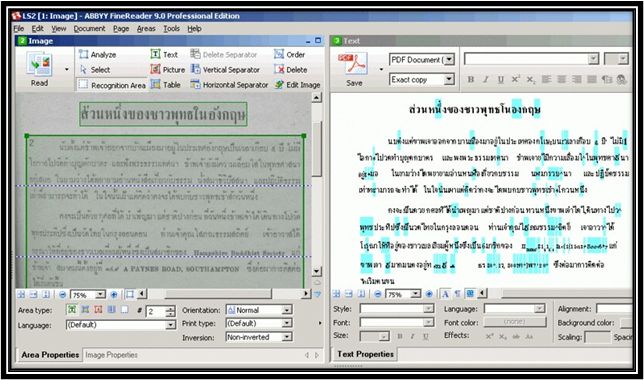
While OCR can save an incredible amount of time, it is not a completely automated system. For printed documents from the 20th-21st century, most programs can guarantee a 95-99% accuracy rate. The same is not true, however, for older documents. OCR software works by recognizing pre-built characters the software was initially programmed to recognize. When a document does not follow that same pattern, the software cannot recognize it. Handwritten documents are a good example of this, in which the same letter may appear differently to the software, depending on how it was written. Some programs, such as ABBYY FineReader, have attempted to resolve this problem by incorporating a training program, which allows users to train the system to read specific types of handwriting. Even still, that training process requires human input, and there is still much work for individuals to put into ensuring that the processed document is accurate. As a result, OCR can be a time-consuming process that still requires plenty of human labor for a project.
Western Biases
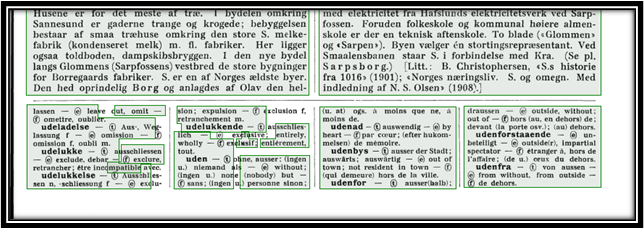
Another key issue with the OCR process is the Western biases that went into the creation of the software. Many common OCR programs were designed to handle projects with Latinized scripts. While helpful for some projects, this left barriers to documents with non-Latinized scripts, particularly from languages commonly used outside the West. While advances have been made on this front, the advancements are still far behind that of Latinized scripts. For example, ABBYY FineReader is one of the few software programs that will scan in non-western languages, but it cannot incorporate its training program when those scripts aren’t Latinized. Adobe Acrobat can also scan documents with languages that use non-Latinized scripts, but its precision is less consistent than with those languages that do.
Addressing the Issues with OCR
Although OCR has performed many amazing tasks, there is still much development needed when it comes to projects related to this aspect of scholarly research. One crucial component when considering taking on an OCR project is to recognize the limitations of the software and to account for that when determining the scope of your project. At this stage, OCR technology is certainly a time-saver and fundamentally changing the possibilities of scholarship, but without human input, these projects fail to make an impact. Likewise, recognizing the inequality of processing for non-western languages in some of the more prevalent OCR software (which several developers have looked to offset by creating OCR programs specifically catered to specific non-Latinized languages). Acknowledging these issues can help us consider the scope of various projects and also allow us to address these issues to make OCR a more accessible field.